real-world프로젝트 Spring 시작하기(5) - 회원가입 만들기 전 설정 Web설정파일 만들기
코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
package com.io.realworld.security;
import com.io.realworld.security.jwt.JwtAuthenticationFilter;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityCustomizer;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.web.SecurityFilterChain;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.HttpStatusEntryPoint;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter;
@Configuration
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebConfig {
private final JwtAuthenticationFilter jwtAuthenticationFilter;
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
@Bean
public WebSecurityCustomizer configure() throws Exception{
return (web) -> web.ignoring().antMatchers("/h2-console/**");
}
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf()
.disable()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/api/users/**").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.disable()
.exceptionHandling().authenticationEntryPoint(new HttpStatusEntryPoint(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED))
.and()
.addFilterBefore(jwtAuthenticationFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
return http.build();
}
}
이 코드를 분석해볼 것이다.
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableWebSecurity와 @Configuration을 통해서 Spring Security 설정할 클래스라고 정의를 한다.
보통 WebSebSecurityConfigurerAdapter을 상속받아서 구현하는데, 현재 필자 버전에서는 WebSebSecurityConfigurerAdapter가 Deprecate되어버려서 직접 필요한것들은 빈으로 생성해야한다.
원래는 여러 configure()함수를 오버라이딩 해주면서 설정을 해줘야했지만 그런것들이 사라졌다.
참고로 Spring boot를 사용하면 해당 어노테이션은 자동으로 세팅되므로 따로 적어주지 않아도 된다길래 나도 지웠다.
@RequiredArgsConstructor
롬복 어노테이션으로 초기화되지 않은 final필드나 @NonNull이 붙은 필드에 대해 생성자를 생성해준다. 이를 통해 JWT관련 필터 클래스를 초기화해준다.
BCryptPasswordEncoder
BCrypt라는 해시 알고리즘을 통해 암호화인코더를 구현한 클래스다.
BCrypy는 반복된 brute-force에도 잘 대응하고 가장 강력한 해시 메커니즘 중 하나라고 한다.
회원가입할 때 패스워드를 암호화해줘야하므로 이것을 Bean으로 등록해준다.
configure()함수
1
2
3
4
@Bean
public WebSecurityCustomizer configure() throws Exception{
return (web) -> web.ignoring().antMatchers("/h2-console/**");
}
WebSecurityCustomizer는 @FunctionalInterface어노테이션이 붙어 있어서 람다표현식을 사용하여 작성해야한다.
WebSecurity 클래스를 커스터마이징하여 이를 반환해야한다.
위의 문법을 통해 h2-console로 들어오는 모든 요청에 대해 인증 필터를 안 타게 해준다.
이는 예전 WebSecurity 설정을 해주는것과 동일하다.
filterChain()함수
위가 예전 WebSecurity 설정을 하는거라면 이함수의 리턴타입은 HttpSecurity 설정을 하는것과 동일하다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf()
.disable()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/api/users/**").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.disable()
.exceptionHandling().authenticationEntryPoint(new HttpStatusEntryPoint(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED))
.and()
.addFilterBefore(jwtAuthenticationFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
return http.build();
}
코드를 보면 antMatchers()라는 함수가 똑같이 쓰인다. 그러면 여기서 반환하는 HttpSecurity와 WebSecurity의 차이점은 뭘까??
HttpSecurity vs WebSecurity
stackoverflow 글을 보면 WebSecurtiy로 설정하면 스프링 시큐리티가 제공하는 다른 기능들도 무시하면서 요청을 받을 수 있다. 예를들면 스프링 시큐리티 컨텍스트를 사용하지 못한다. 그리고 저 코드에서 /h2-console url을 기준으로 해당 url로 요청으로 들어왔을때 XSS 어택, 스니핑, Cross-Site-Scripting과 같은 공격에 방어할 수 없다.
그러면 HttpSecurity는 스프링 시큐리티가 제공하는 기능들을 쓸 수 있어서 위와 같은 공격에 대응이 가능하다. HttpSecurity로 설정한 것들은 인증에 대해서 무시하는것이고, 필터는 다 거치기에 필터를 거치는 비용이 있을 수 밖에 없다.
그렇기에 WebSecurity에 등록하는 것들은 보통 이미지나, js파일과 같은 인증/인가 정보가 필요없는 것들을 등록하고 사용한다고 한다.
문법설명
함수들을 설명했으니 함수 안에 있는 것들이 어떤것을 나타내는지 알아볼 것이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
http.csrf() - 1
.disable() - 2
.authorizeRequests() - 3
.antMatchers("/api/users/**").permitAll() - 4
.anyRequest().authenticated() - 5
.and() -6
.formLogin() - 7
.disable() - 8
.exceptionHandling().authenticationEntryPoint(new HttpStatusEntryPoint(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED)) - 9
.and() - 10
.addFilterBefore(jwtAuthenticationFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class); - 11
return http.build(); - 12
- 1, 2 : csrf().disable()란 csrf()란 것을 사용하지 않겠다는 것인데, CSRF라는 것에 대해 알고 있어야한다.
CSRF란 세션과 쿠키의 특징을 이용한 공격방법인데, 사용자가 로그인이나 요청을 보냈을 경우 서버에서 sessionID를 주고 이를 사용자 쿠키에 저장하게 되는데, 공격자가 악성 스크립트를 누르도록 유도하여 사용자 브라우저에 저장 되어있는 sessionID를 이용하여 서버에 요청을 보내는 것이다. 서버는 sessionID를 통해 정상 사용자로 판단하고 요청을 처리하게 된다.
보통 stateless한 RestAPI에서는 쿠키나 세션을 사용하지 않고, 이 프로젝트도 JWT토큰을 사용하기에 csrf보호가 따로 필요없어서 disable처리를 했다.
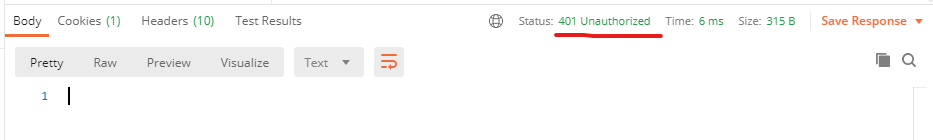
그렇다해서 이를 따로 명시해주지 않는다면 Spring Security는 자동으로 csrf보호를 하기 때문에 어떤 요청에서도 csrf토큰이 포함되지 않아서 401 Unauthorized 상태를 반환할 것이다.
csrf를 직접 생성하여 해결하는 방법은 이 블로그를 참조하면 좋다.
3, 4 :
authorizeRequests()는 HttpServletRequest에 따라 접근을 제한한다는 의미이다. 뒤에 있는 문법들이 제한하는것을 도와줄 것이다.antMatchers(url).permitAll()은 적힌 url에 들어오는 요청에 대해서는 아무 인가된 사용자가 아니여도 접근이 가능하게 지정한다. 참고로 url뿐만 아니라 Http Method도 적어줄 수 있고 혼용하여 사용할 수 있다.5 :
antMatchers().permitAll()는 어떤 요청에 대해서도 인증된 사용자만 접근허용하도록 한다는 제한을 건다.
혼자 궁금해서
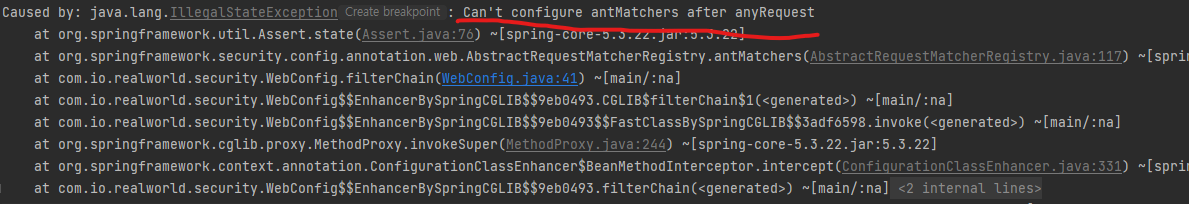
antMatchers().permitAll()와anyRequest().authenticated()의 순서를 바꿔서 써봤다. 우선순위가 antMatchers 먼저일까 anyRequest가 먼저일까 궁금해졌기 때문이다. 결과는 에러가 발생한다. 그리고 친절하게 알려준다. antMatchers는 anyRequest뒤에 나올 수 없단다.
6 : and()는 상위 메소드들을 연결하기 위해 필요한 연결점이라고 생각하면 된다.
7,8 : 사용자 정의 로그인 기능과 로그아웃 기능을 가진 상위 메소드라는데,
loginPage(url)처럼 login페이지 경로를 알려줄 수도 있고 로그인에 실패했을때 페이지, 성공했을때 페이지를 따로 또 지정해줄 수 있다. 이 기능말고 다양한 기능을 수행한다. 또한 보안 검증을 form기반으로 할 것이라고 하는데, 이 프로젝트에서는 그러지 않으므로 disable처리를 해주었다.9 :
exceptionHandling()는 예외가 발생했을때 핸들링할 수 있게 도와준다. 이 놈은ExceptionHandlingConfigurer를 받아야하고, 이를 만들기 위해서는authenticationEntryPoint()함수를 사용한다.
이 함수의 구현을 보면
1
2
3
4
public ExceptionHandlingConfigurer<H> authenticationEntryPoint(AuthenticationEntryPoint authenticationEntryPoint) {
this.authenticationEntryPoint = authenticationEntryPoint;
return this;
}
AuthenticationEntryPoint타입의 객체를 받는데, HttpStatusEntryPoint 클래스는 AuthenticationEntryPoint를 상속받아 구현되었기에 인자로 쓸 수 있다. 다행스럽게도 HttpStatusEntryPoint는 비교적 간단하게 구현되어있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
public final class HttpStatusEntryPoint implements AuthenticationEntryPoint {
private final HttpStatus httpStatus;
/**
* Creates a new instance.
* @param httpStatus the HttpStatus to set
*/
public HttpStatusEntryPoint(HttpStatus httpStatus) {
Assert.notNull(httpStatus, "httpStatus cannot be null");
this.httpStatus = httpStatus;
}
...
}
간단하게 httpStatus만 넘겨주면 알아서 인증에 실패했을때 인자로 넘긴 httpStatus에러를 발생시킨다는 것이다. 이는 메세지를 넘기도록 커스텀마이징도 가능하다. 하단에 있는 Reference를 참고하면 된다.
아무튼 나는 HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED를 넘겨 401 UnAuthorized를 발생시키도록 설정해놨다.
- 11 : 말그대로 필터를 등록한다는 것이다.
1
addFilterBefore(filter A, filter B.class): filter A 추가 (filter B보다 우선)
그렇기에 향후 작성할 jwt관련 필터는 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter라는 필터보다 먼저 실행될 것이다.
그러면 또 새로운 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter에 대해 간단히 알 필요가 있다.
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
코드 자체는 어렵지 않으나 내부동작이 어렵다. 간단히만 알아볼 것이다.
이것은 jwt토큰만들때 + user정보 찾을때와 연동이 되어야하기에 대략적인 느낌만 적어둘것이다. 향후 위의 두 가지를 다룰때 상세히 적어보도록 하겠다.
코드를 까보면
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
public class UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter extends AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter {
...
@Override
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws AuthenticationException {
if (this.postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException("Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
}
String username = obtainUsername(request);
username = (username != null) ? username.trim() : "";
String password = obtainPassword(request);
password = (password != null) ? password : "";
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.unauthenticated(username,
password);
// Allow subclasses to set the "details" property
setDetails(request, authRequest);
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
이렇게 되어있다. POST요청이 아닌경우에는 에러를 발생시킨다. 문제는 String username = obtainUsername(request);이 구문이다.
1
2
3
protected String obtainUsername(HttpServletRequest request) {
return request.getParameter(this.usernameParameter);
}
이렇게 이놈은 헤더에서 값을 찾는데, 어떻게 JSON으로 요청을 보내는데 받는다는 말인가?
이는 나중에 작성할 jwt필터에서 이미 인증정보를 넣었기 때문이라고 말할 수 있다.
jwt 필터에는 다음과 같은 코드가 있다.
1
2
Authentication auth = jwtService.getAuthentication(jwt);
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(auth);
Authentication이라는 객체를 만들어서 시큐리티 컨텍스트에 넣고있다. 기존 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter에서는 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken()메소드를 호출하여 컨텍스트에 넣고 있는데, 내가 만든 jwtService.getAuthentication()을 보면
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
...
public Authentication getAuthentication(String jwtToken) {
UserDetails userDetails = userServiceDetail.loadUserByUsername(getEmail(jwtToken));
User user = (User)userDetails;
UserAuth authenticatedUser = UserAuth.builder()
.username(user.getUsername())
.id(user.getId()).build();
return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(authenticatedUser,"", userDetails.getAuthorities());
}
유저객체로 토큰을 만들어서 리턴하고 jwt필터에서는 이를 시큐리티 컨텍스트에 넣고 있는것이다.
실제로 jwt필터의 auth를 찍어보면
1
2022-10-11 23:42:53.205 INFO 14560 --- [nio-8080-exec-2] c.i.r.s.jwt.JwtAuthenticationFilter : auth: UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken [Principal=com.io.realworld.domain.aggregate.user.dto.UserAuth@216ee17a, Credentials=[PROTECTED], Authenticated=true, Details=null, Granted Authorities=[]]
이렇게 출력되는것을 볼 수 있다.
사실 이를 이해하려면 Spring-Security 내부동작에 대해 좀 더 학습해야하는 것 같다.
결론
Spring Web설정에 대해 이해하려고 했다.
고작 구현은 30줄인 코드를 해석하는데 vscode 기준 300줄이 넘는 설명을 덧붙였다.
그리고 글을 작성하는데 2일이 걸렸다.. 부족한 부분은 따로 회사 점심시간에 찾아보고 그래도 글이 많이 부족하다.
그리고 Spring Security는 진짜 방대하다는것을 다른 문서들을 찾아보면서 느꼈다.
내가 글을 좀 더 잘 썼다면 정리가 더 잘되고 깔끔한 글이 되었을텐데 아쉽다.
Reference
- https://engineering-skcc.github.io/spring-security-series/Spring-Security-guide/ SK C&C Tech 블로그
- https://spring.io/blog/2022/02/21/spring-security-without-the-websecurityconfigureradapter
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/56388865/spring-security-configuration-httpsecurity-vs-websecurity 스택오버플로우 WebSecurity vs WebSecurity
- https://zzang9ha.tistory.com/341 CSRF에 대하여
- https://catsbi.oopy.io/c0a4f395-24b2-44e5-8eeb-275d19e2a536 Spring Security 로그인 상세정리글.
- https://sas-study.tistory.com/362 exceptionHandling 커스텀마이징
- https://ckinan.com/blog/spring-security-credentials-from-json-request/ 필터 동작방식 조금
현재 이 프로젝트는 vue.js + vite + vuex + Spring boot, Spring Data JPA + Spring Security 를 이용하여 real-world 데모버전을 제작완료하였습니다. https://github.com/kkminseok/real-world-springboot