leetcode(리트코드)2월 06일 challenge199-Binary Tree Right Side View
leetcode(리트코드)2월 06일 challenge199-Binary Tree Right Side View
leetcode 199 - Binary Tree Right Side View문제입니다.
1. 문제
https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-right-side-view/
2. Input , Output
Constraints:
3. 분류 및 난이도
Medium 난이도 문제입니다.
leetcode Top 100 Liked의 문제입니다.
또한 2월 6일 Challenge 문제입니다.
4. 문제 해석
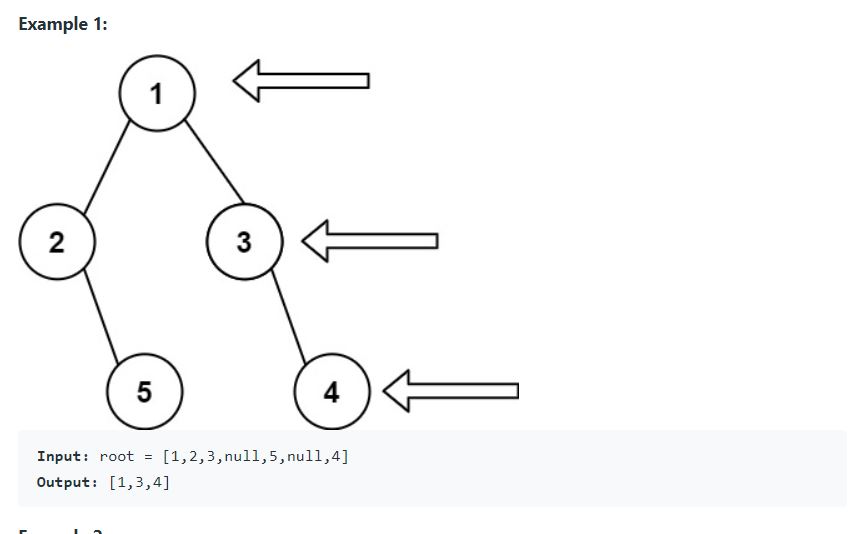
- 오른쪽에서 트리를 봤을 때의 모습, 위 노드 -> 밑 노드 값을 벡터에 넣어 리턴합니다. 예를 들어 1,2,3,4 가 주어지면 1,3,4를 리턴해야합니다.
5. code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> result;
bool depth[101];
void order(TreeNode* root,int _depth)
{
if(root->right!=nullptr)
{
if(depth[_depth]==false)
{
result.push_back(root->right->val);
depth[_depth]=true;
}
order(root->right,_depth+1);
}
if(root->left!=nullptr)
{
if(depth[_depth]==false)
{
result.push_back(root->left->val);
depth[_depth]=true;
}
order(root->left,_depth+1);
}
}
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
memset(depth,false,sizeof(depth));
if(root!=nullptr)
{
result.push_back(root->val);
depth[0]=true;
order(root,1);
}
return result;
}
};
6. 결과 및 후기, 개선점
시간(67%)
0ms(100%) 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL)
return vector<int> {};
vector<int> res, v;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
q.push(NULL);
while(q.size() > 1)
{
TreeNode* curr = q.front();
q.pop();
if(curr == NULL)
{
q.push(NULL);
res.push_back(v[v.size() - 1]);
v.clear();
continue;
}
v.push_back(curr->val);
if(curr->left)
q.push(curr->left);
if(curr->right)
q.push(curr->right);
}
res.push_back(v[v.size() - 1]);
return res;
}
};
이 코드에서 NULL을 넣는 이유는 구분하기 위해서입니다.
예를 들어서 1,2,3,4가 들어오면 1 NULL 2 3 NULL 4 이렇게 구분하여 NULL보다 한단계 이전값을 vector에 너헝 반환합니다.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.