leetcode(리트코드)2-Add Two Numbers
leetcode(리트코드)2-Add Two Numbers
leetcode 2 - Add Two Numbers 문제입니다.
1. 문제
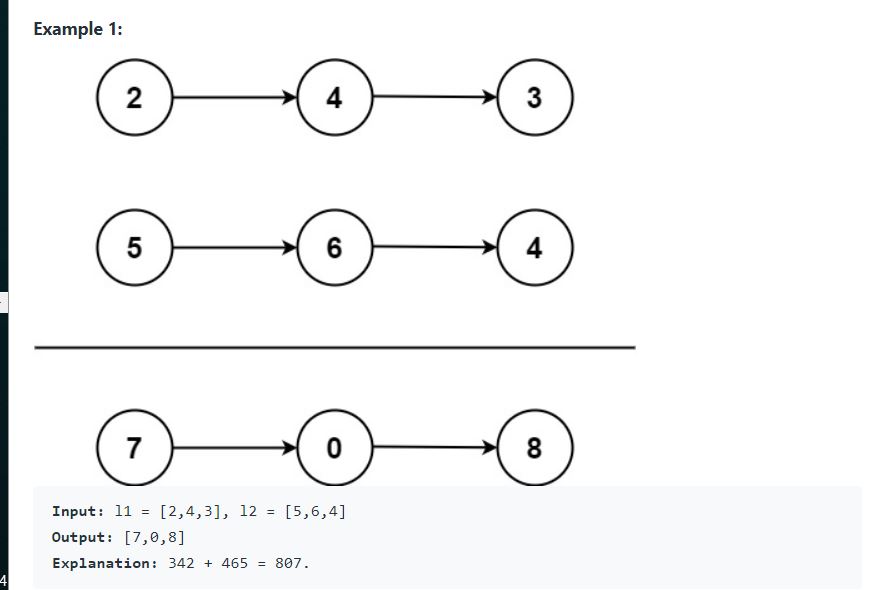
https://leetcode.com/problems/add-two-numbers/
2. Input , Output
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in each linked list is in the range [1, 100].
- 0 <= Node.val <= 9
- It is guaranteed that the list represents a number that does not have leading zeros.
3. 분류 및 난이도
Medium 난이도 문제입니다.
leetcode Top 100 Liked의 두 번째 문제입니다.
4. 문제 해석
- 영어를 잘 못해서 해석에서 고생을 좀 했습니다.
- 일단 int형이든 long long형이든 단순계산으로 풀기는 힘듭니다. 최대 100자리까지 들어오므로 표현할 수 있는 bit수를 넘어버리기 때문입니다.
- 그래서 string으로 표현하여 계산하기로 생각했습니다.
input으로 처음에 ‘0’이 안들어올 줄 알았는데 들어오길래 해맸습니다..
- 아무튼 string으로 바꿔서 자릿수 하나하나 더해줬습니다.
- 만약 어떤 짧은 문자열을 먼저 돌았으면 나머지 문자열을 List에 추가하기 위해 while문을 만들고 만약 돌았음에도 불구하고 carry가 남는다면 처리해주는 로직으로 짰습니다.
5. code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode* result = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* location=result;
string x = "";
string y = "";
while(l1!=nullptr)
{
x+=(to_string(l1->val));
l1=l1->next;
}
while(l2!=nullptr)
{
y += (to_string(l2->val));
l2=l2->next;
}
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int carry=0;
while(i<x.size() && j< y.size())
{
int sum = (x[i]-'0') + (y[i]-'0')+carry;
carry= sum/10;
sum%=10;
ListNode* newNode = new ListNode(sum);
result->next= newNode;
result=result->next;
cout<<sum<<'\n';
++i;
++j;
}
cout<<"dasd"<<carry<<'\n';
while(j<y.size())
{
int sum = (y[j]-'0') + carry;
carry= sum/10;
sum%=10;
cout<<sum<<'\n';
ListNode* newNode = new ListNode(sum);
result->next= newNode;
result=result->next;
++j;
}
while(i<x.size())
{
int sum = (x[i]-'0') + carry;
carry= sum/10;
sum%=10;
cout<<sum<<'\n';
ListNode* newNode = new ListNode(sum);
result->next= newNode;
result=result->next;
++i;
}
if(carry!=0)
{
ListNode* newNode = new ListNode(1);
result->next= newNode;
result=result->next;
}
return location->next;
}
};
python
개선된 코드를 python으로 재작성 하였습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
sum = 0
carry = 0
x1 = ListNode()
x2 = ListNode()
x3 = ListNode()
x3 = l1
while(l1 != None or l2!=None or carry != 0):
if(l1==None):
l1 = ListNode(0)
x1.next=l1
if(l2==None):
l2 = ListNode(0)
x2.next=l2
sum= l1.val + l2.val +carry
carry = sum//10
l1.val = sum%10
x1=l1
x2=l2
l1=l1.next
l2=l2.next
return x3
6. 결과 및 후기, 개선점
시간(89%)
빠른 코드를 보니 포인터를 좀 더 잘 활용했으면 쉽게 풀었을 것이라는 생각을 했습니다.. ㅠ
처음에는 재귀를 생각하긴 했는데, 짜다가 골치아파서 포기했습니다.
빠른 시간 코드(4ms 99%)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
int sum=0, carry=0;
ListNode *x1, *x2, *x3;
//x3이 가리킴
x3=l1;
//들어온 리스트들이 null이 아니고 carry가 0이아니면
while(l1!=NULL||l2!=NULL||carry!=0){
//만약 빈 리스트를 가리키고 있으면 임의로 0을 넣어버려서 계산하기 쉽게(0+어떤 수) 만들어버림!!
if(l1==NULL){
l1=new ListNode(0);
x1->next=l1;
}
if(l2==NULL){
l2=new ListNode(0);
x2->next=l2;
}
//계산하는 과정
sum=l1->val+l2->val+carry;
carry=sum/10;
l1->val=sum%10;
//x1, x2는 l1,l2의 다음 노드를 가리킨다.
x1=l1;
x2=l2;
l1=l1->next;
l2=l2->next;
}
return x3;
}
};
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.