FastAPI 공식문서 따라하기[25] - Body Updates
https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/tutorial/body-updates/ 공식문서 따라하는 글
☑️ Update Replacing with PUT
보통 HTTP의 put라는 것을 통하여 객체를 수정할 수 있도록 한다.
전의 포스팅에서 사용한 jsonable_encoder를 통해 들어온 값들에 대해 JSON 타입으로 바꿔 저장할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
from fastapi import FastAPI
from fastapi.encoders import jsonable_encoder
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str | None = None
description: str | None = None
price: float | None = None
tax: float = 10.5
tags: list[str] = []
items = {
"foo": {"name": "Foo", "price": 50.2},
"bar": {"name": "Bar", "description": "The bartenders", "price": 62, "tax": 20.2},
"baz": {"name": "Baz", "description": None, "price": 50.2, "tax": 10.5, "tags": []},
}
@app.get("/items/{item_id}", response_model=Item)
async def read_item(item_id: str):
return items[item_id]
@app.put("/items/{item_id}", response_model=Item)
async def update_item(item_id: str, item: Item):
update_item_encoded = jsonable_encoder(item)
items[item_id] = update_item_encoded
return update_item_encoded
@app.put을 통해 객체에 대한 정보를 바꿔쓸 수 있다.
☑️ Warning about replacing
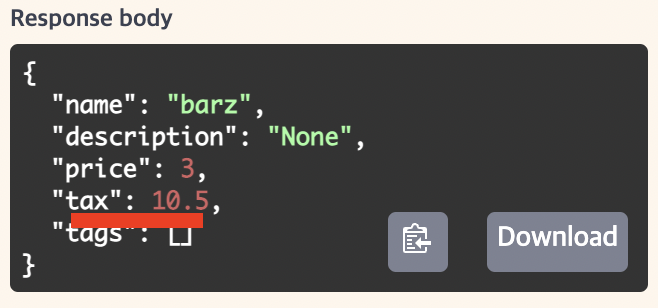
만약 위의 “bar”객체를 다음과 같이 수정하고 싶어서 body에 다음 값을 넘겨본다고 가정하자.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
{
{
"name": "barz",
"description": "None",
"price": 3,
"tags": []
}
}
문제는 “bar”에 설정된 tax필드에 대한 값(20.2)를 지정하지 않아서 default value인 10.5가 들어갈 것이다.
결과값
☑️ Partial updates with PATCH
HTTP의 PATCH를 사용해서 사용자가 필요한 데이터만 수정하고 나머지는 그대로 유지할 수 있게 한다.
PUT에 비해PATCH는 인지도가 낮다. 흔히PUT이 많이 사용되며, 부분적 업데이트에서도 사용된다. 사용하는것은 자유지만,FastAPI는 어떠한 제한을 도입하지 않았다고 한다. 그래서 이번 챕터에서 왜 그렇게 제한을 두지 않았는지 알려준다고 한다.
☑️ Using Pydantic’s exclude_unset parameter
만약 부분적 업데이트가 필요하면 Pydantic’s model의 .dict()에 있는 exclude_unset를 이용하면 된다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
from fastapi import FastAPI
from fastapi.encoders import jsonable_encoder
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str | None = None
description: str | None = None
price: float | None = None
tax: float = 10.5
tags: list[str] = []
items = {
"foo": {"name": "Foo", "price": 50.2},
"bar": {"name": "Bar", "description": "The bartenders", "price": 62, "tax": 20.2},
"baz": {"name": "Baz", "description": None, "price": 50.2, "tax": 10.5, "tags": []},
}
@app.get("/items/{item_id}", response_model=Item)
async def read_item(item_id: str):
return items[item_id]
@app.patch("/items/{item_id}", response_model=Item)
async def update_item(item_id: str, item: Item):
stored_item_data = items[item_id]
stored_item_model = Item(**stored_item_data)
update_data = item.dict(exclude_unset=True)
updated_item = stored_item_model.copy(update=update_data)
items[item_id] = jsonable_encoder(updated_item)
return updated_item
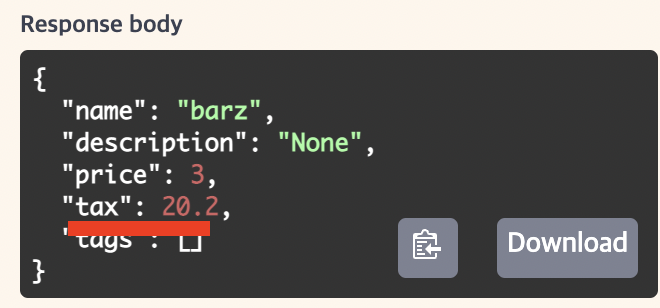
이렇게 하면 default value는 제외하고 설정된 데이터만 가지고 dict자료형을 만든다.
결과
☑️ Using Pydantic’s update parameter
위의 구문을 보면 stored_item_model.copy(update=update_data)에서 update는 Pydantic에서 제공하는 것이다.
위의 내용들을 요약하자면
PATCH를PUT대신 사용.- 저장된 데이터를 찾음.
- Pydantic model에 저장된 데이터를 넣음.
exclude_unset을 이용하여dict을 default value를 제 하고 생성.- 위의 Pydantic model의 Copy를 이용하여 속성값들을 부분적 업데이트(
update구문 이용) jsonable_encoder를 이용하여 DB에 저장할 수 있는 자료형으로 바꿈.- DB에 저장
- 수정된 객체를 반환.