백엔드 웹 개발 노트6.3 - Spring MVC HTTP Request
1. HTTP 요청 파라미터 - 쿼리파라미터, HTML FORM
클라이언트에서 서버로 요청 데이터를 전달할 때는 주로 다음 3가지 방법을 사용한다.
- GET - 쿼리 파라미터
- 메시지 바디 없이, URL의 쿼리 파라미터에 데이터를 포함해서 전달
- /url?username=kms&hegiht=178
- POST - HTML Form
- content-type:application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- 메시지 바디에 쿼리 파라미터 형식으로 전달함.
- HTTP message body에 데이터를 직접 담아서 요청
- HTTP API에 주로 사용된다. JSON, XML, TEXT
- 데이터 형식은 주로 JSON이 사용된다.
1.1 GET,쿼리 파라미터로 전송.
자바 파일을 만들자.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
package hello.springmvc.basic.request;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@Slf4j
@Controller
public class RequestParamController {
//기본적인 형태
@RequestMapping("/kms-request-param-v1")
public void requestParamv1(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
String username = request.getParameter("username");
int height = Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("height"));
log.info("username = {} , height = {}",username,height);
response.getWriter().write("ok");
}
}
기본적인 예제이다. http://localhost:8080/kms-request-param-v1?username=kms&height=178 으로 들어가면 된다.
1.2 Post로 Form 전송
전송하기 위해 html 파일을 만들어야한다.
경로는 main/resources/static/basic/kms-from.html 이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/kms-request-param-v1" method="post">
username: <input type="text" name="username" />
height: <input type="text" name="height" />
<button type="submit">전송</button>
</form>
</body>
</html>
<localhost:8080/kms-request-param-v1> 으로 가면 입력폼에 입력하고 전송 버튼을 누르면
위에서 작성한 java에서 요청값을 받아 로그에 잘 찍고 잘 받아온다.
쿼리 파라미터와 다른 점은 뭘까?
url에 데이터를 넣냐 html에 데이터 넣냐의 차이다.
보안적으로 GET Query보다는 Post Form이 더 좋아보이지 않는가?
GET은 데이터를 보낸다는 것 보다는 조회목적으로 쓰자.
2. HTTP 요청 파라미터 - @RequestParam
@RequestParam 애노테이션을 이용해서 요청 파라미터를 관리해보자.
가장 기본적인 형태는 다음과 같다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
package hello.springmvc.basic.request;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@Slf4j
@Controller
public class RequestParamController {
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/kms-request-param-v2")
public String requestParamV2(
@RequestParam("username") String myname,
@RequestParam("height") int myheight
){
log.info("username = {} , height = {}",myname,myheight);
return "ok";
}
}
@ResponseBody 를 사용해준 이유는 @Controller 애노테이션 때문에 리턴값으로 지정한 “ok”를 논리적 뷰 이름으로 판단하지 않게끔 하기 위해서이다. 이렇게 설정하면 @RestController 처럼 HTTP message body에 리턴값을 넣어버려 반환한다.
뒤에서 설명할것!!
만약 HTTP 요청 파라미터 이름이 변수 이름과 같다면 @RequestParam() 속성값을 생략할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
package hello.springmvc.basic.request;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@Slf4j
@Controller
public class RequestParamController {
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/kms-request-param-v3")
public String requestParamV3(
@RequestParam String username,
@RequestParam int height
){
log.info("username = {} , height = {}",username,height);
return "ok";
}
}
즉 url에서 요청을 보낼때 http://localhost:8080/kms-request-param-v3?username=kms&height=178 이런식으로 파라미터 이름과 @RequestParam 의 변수값이 같아야 한다.
심지어 위와 같은 상황에서 @RequestParam 을 생략할수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
package hello.springmvc.basic.request;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@Slf4j
@Controller
public class RequestParamController {
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/kms-request-param-v4")
public String requestParamV4(String username,int height){
log.info("username = {} , height = {}",username,height);
return "ok";
}
}
이러한 방식은 팀원들끼리 협의가 되어있어야 한다. 너무 줄여서 헷갈릴수 있기 때문이다. @RequestParam 을 명시하여 요청 파라미터에서 데이터를 읽는 다는 것을 알 수 있다.
2.1 파라미터 필수 여부 - requestParamRequired
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
package hello.springmvc.basic.request;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@Slf4j
@Controller
public class RequestParamController {
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/kms-request-param-required")
public String requestParamRequired(
@RequestParam(required = true) String username,
@RequestParam(required = false) int height
){
log.info("username = {} , height = {}",username,height);
return "ok";
}
}
@RequestParam 의 속성 값으로 ‘required = true’, ‘required = false’가 있다.
딱봐도 username은 꼭 요청파라미터로 들어와야하고, height는 요청 파라미터로 없어도 된다는걸 알수 있다.
다만, 여기서 주의할 점이 있다.
요청 파라미터로,
username=&height=178
username&height=178
라는 값이 들어오면 400(Bad request)가 뜰까??
“ok”가 뜬다. 빈문자로 넣어버리기 때문이다.
만약 height도 required = true로 놓고 ‘height=’나 ‘height’까지만 넣으면 어떻게 될까?
400 error가 뜬다. 이유는 int로 선언해서 그렇다. int로 선언한 변수에는 NULL값을 넣지 못한다.
여기서 필요한건 requestParamDefault 이다.
2.1.1 기본값 적용 - requestParamDefault
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
package hello.springmvc.basic.request;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@Slf4j
@Controller
public class RequestParamController {
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/kms-request-param-required")
public String requestParamRequired(
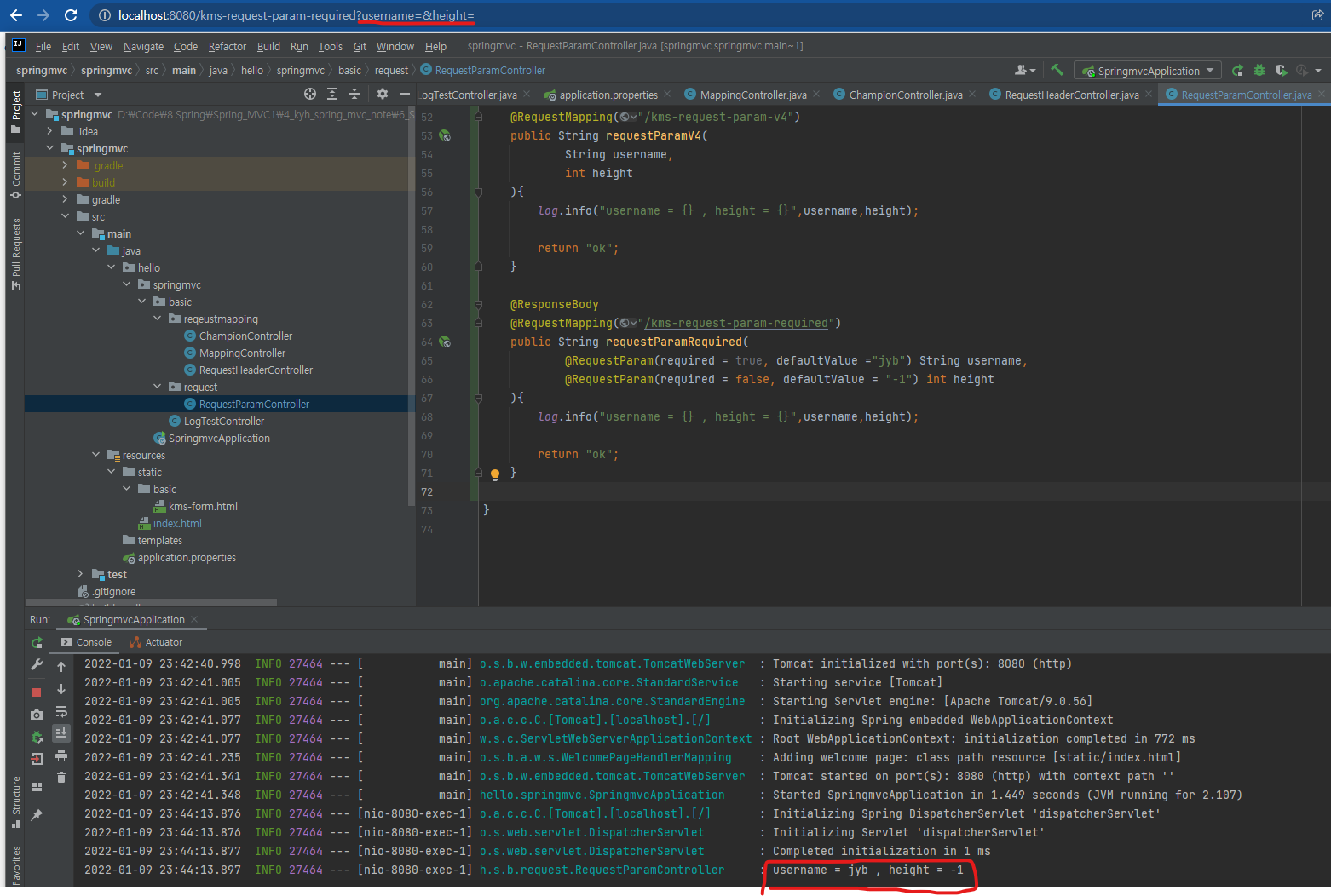
@RequestParam(required = true, defaultValue ="jyb") String username,
@RequestParam(required = false, defaultValue = "-1") int height
){
log.info("username = {} , height = {}",username,height);
return "ok";
}
}
어떤 의미인지 직관적으로 알수 있다.
요청 파라미터가 비어있다(NULL)면 username에는 ‘jyb’를 넣어주고, height에는 ‘-1’를 넣어준다.
또한 파라미터를 Map으로 조회할 수 있다.
2.2 requestParamMap
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
package hello.springmvc.basic.request;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Map;
@Slf4j
@Controller
public class RequestParamController {
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/kms-request-param-map")
public String requestParamMap(@RequestParam Map<String,Object> paramMap){
log.info("username = {} , height = {}",paramMap.get("username"),paramMap.get("height"));
return "ok";
}
}
파라미터의 값이 1개가 확실하다면 Map 을 사용해도 되지만, 그렇지 않다면 MultiValueMap 을 사용하자.!
3. HTTP 요청 파라미터 - @ModelAttribute
실제 개발을 하다보면 요청파라미터를 받아서 필요한 객체를 만들고 그 객체에 값을 넣어줘야 한다. 보통 다음과 같이 코드를 작성할 것이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
package hello.springmvc.basic;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class BmiData {
private String name;
private int height;
private int weight;
}
BMI계산에 필요한 user객체이다.
3.1 @Data
- 롬복에서 제공하는 애노테이션으로 @Getter, @Setter, @ToString, @EqualsAndHashCode, @RequiredArgsConstructor를 자동으로 제공한다.
@ModelAttribute를 적용하면 더 편리하게 파라미터를 받을수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
package hello.springmvc.basic.request;
import hello.springmvc.basic.BmiData;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Map;
@Slf4j
@Controller
public class RequestParamController {
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/kms-model-attribute-v1")
public String modelAttributeV1(@ModelAttribute BmiData bmiData){
log.info("username = {} , height = {} , weight = {}",bmiData.getName(),bmiData.getHeight(),bmiData.getWeight());
return "ok";
}
}
결과
보기에 너무 간편하지만 좀 더 직접적인 이유가 없을까?
만약 저 3가지 변수를 RequestParam으로 받아온다면 코드가 얼마나 길어질지 감이 잡히는가?
그렇기에 객체에 자동으로 넣어주는 @ModelAttribute 가 편한것이다.
참고로 스프링 MVC는 @ModelAttribute 가 있으면 다음과 같이 실행한다.
- BmiData 객체 생성
- 요청 파라미터의 이름으로 BmiData 객체의 프로퍼티를 찾는다. 해당 프로퍼티의 setter를 호출해서 파라미터의 값을 바인딩한다.
또한, 객체의 값을 수정하면 set~()함수가 호출되고 값을 조회하면 get~()함수가 호출된다.
심지어 위 코드에서 @ModelAttribute 를 생략할 수 있다.
@RequestParam 도 생략이 가능해서 스프링은 생략시 다음과 같은 규칙을 적용한다.
- String, int, Integer 같은 단순 타입 = @RequestParam 지정.
- 나머지는 @ModelAttribute(단, argument resolver로 지정해둔 타입 외 ex] HttpServeltResponse 등)