Spring - @SpringbootApplication가 뭘까 1편 메타어노테이션까지
개요
@SpringbootApplication에 대해 설명해 달라는 질문을 받았다.
당연히 main에 붙어있고 그 이후에 볼 일이 없어서 당연시하게 쳐다도 안 보게 되었다.(사실 의식하지 않으면 있는지도 몰랐음.)
boot를 쓴다하면 다 붙어있는데 답변을 못했고 부끄러워서 정리를 해보려고 한다.
뜻
부트의 가장 기본적인 설정을 해준다고 알려져 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
...
}
으로 되어있는데 어노테이션 하나씩 까보도록 하자.
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
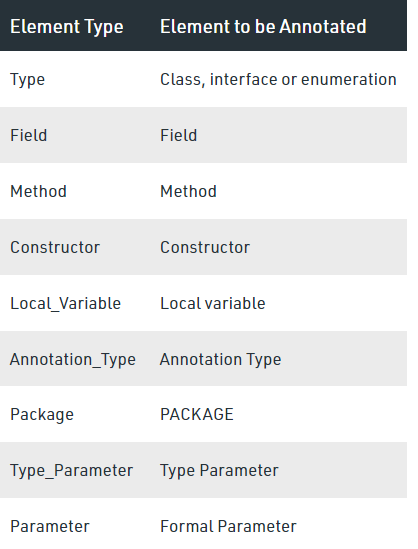
Target 어노테이션은 이 어노테이션이 붙을 수 있는 타입에 대해 지정한다.
위 표를 보면 Type은 Class, Interface, enumeration에 붙을 수 있다고 써있다.
즉, @SpringBootApplication어노테이션은 우리가 프로젝트로 생성한 main을 감싸고 있는 클래스 위에 붙어있으므로 맞게 부착되었다고 할 수 있다.
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
Retention의 소스를 까보면
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Indicates how long annotations with the annotated interface are to be retained. If no Retention annotation is present on an annotation interface declaration, the retention policy defaults to RetentionPolicy.CLASS.
A Retention meta-annotation has effect only if the meta-annotated interface is used directly for annotation. It has no effect if the meta-annotated interface is used as a member interface in another annotation interface.
Since:
1.5
Author:
Joshua Bloch
jls
9.6.4.2 @Retention
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
public @interface Retention {
RetentionPolicy value();
}
이렇게 되어있다. Target이 ANNOTATION_TYPE으로 되어있어서 결국 @Retention은 어노테이션에만 붙을 수 있다.
윗 주석을 읽어보면 어노테이션의 설명을 볼 수 있다. 어노테이션을 어디까지 살려둘 지를 결정하며 디폴트값은 CLASS이다. RetentionPolicy값을 넘기면서 어노테이션 메모리 범위를 정해주는 것인데, 이는 enum으로 되어 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
// RetentionPolicy enum
public enum RetentionPolicy {
SOURCE,
CLASS,
RUNTIME
}
SOURCE, CLASS, RUNTIME을 넘길 수 있으며 주석으로 살아있는 시점이 적혀져 있다.
이를 이해하려면 JVM 동작방식에 대해 알고 있어야한다.
- SOURCE : complie될 때 어노테이션을 메모리에서 해제. 즉, 소스코드(.java)까지만 남아있는다.
- CLASS : .class파일에 어노테이션을 기록, 이후 메모리에서 해제. 즉, 런타임때는 남아있지 않음.
- RUNTIME : RUNTIME때까지 살아있는 어노테이션
https://jeong-pro.tistory.com/234 포스팅의 댓글을 보면 이해가 빠르다.
결론은 @SpringBootApplication은 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)이므로 런타임때까지 살아있는다.
개인적인 생각입니다.
개인적인 생각으로 왜 런타임때까지 살아있어야하냐면 런타임때까지 살아있으면 어노테이션의 정보를 뽑아쓸 수 있는데(Reflection) 컴포넌트 스캔은 런타임때 어노테이션의 정보를 가지고 스캔을 돌리므로 @SpringBootApplication도 런타임때까지는 살아있어야하는 것이라는 추측이다.
@Documented
이 어노테이션은 자바doc로 API를 만들때 해당 어노테이션에 대한 설명도 추가해주는 어노테이션이다.
@Inherited
상속받은 클래스에도 어노테이션 속성이 붙는다.
보통 main을 포함하는 클래스는 하나이고 이를 상속받을 일은 없기에 @Inherited가 붙어있는 이유를 모르겠어서 생각해봤지만.. 프로젝트가 좀 더 커지면 그런 일이 생기겠지?.. 좀 더 생각이 필요하다.
예제 : https://hongsii.github.io/2018/12/12/java-annotation/
여기까지는 메타 어노테이션이다. 그래서 해석하는데 어려움은 없었다.
@SpringBootConfiguration
이 또한 들어가보면 다음처럼 코드가 되어있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
/**
* Indicates that a class provides Spring Boot application
* {@link Configuration @Configuration}. Can be used as an alternative to the Spring's
* standard {@code @Configuration} annotation so that configuration can be found
* automatically (for example in tests).
* <p>
* Application should only ever include <em>one</em> {@code @SpringBootConfiguration} and
* most idiomatic Spring Boot applications will inherit it from
* {@code @SpringBootApplication}.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @author Andy Wilkinson
* @since 1.4.0
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Configuration
@Indexed
public @interface SpringBootConfiguration {
@AliasFor(annotation = Configuration.class)
boolean proxyBeanMethods() default true;
}
기본으로 제공되는 메타 어노테이션은 위에서 다 설명했고 특이한점이 없다. @Configuration이 붙어있는데 이는 환경설정 빈을 표현하는 어노테이션이다.
맨위의 설명 주석을 보면 @Configuration을 대신 쓸 수 있다고 써 있다.
그리고 그 밑에 ‘@SpringBootConfiguration’ 어노테이션은 하나만 붙어있을 수 있고, 이는 ‘@SpringBootApplication’어노테이션이 상속한다고 되어있는데..
어떤 글에서는 계층을 주기 위함이 아니냐라고 써있다.
1
2
3
@SpringBootApplication
-------> @SpringBootConfiguration
-------> @Configuration
구성을 자동으로 찾아준다는게 일반 @Cofiguration과 다른점이라고 한다. 이는 단위테스트나 통합테스트를 작성할때 유용하다고는 써있지만..
그 방식은 모르겠지만 일단 뒤로 넘어가면 힌트가 있을 수 있다. 그래서 다음부분을 보겠다.
그러면 @Indexed는 무엇인가??
JavaDoc를 읽어보면 굉장히 어렵게 설명이 되어있다..
1
2
3
4
5
6
Indicate that the annotated element represents a stereotype for the index.
The CandidateComponentsIndex is an alternative to classpath scanning that uses a metadata file generated at compilation time. The index allows retrieving the candidate components (i.e. fully qualified name) based on a stereotype. This annotation instructs the generator to index the element on which the annotated element is present or if it implements or extends from the annotated element. The stereotype is the fully qualified name of the annotated element.
Consider the default Component annotation that is meta-annotated with this annotation. If a component is annotated with Component, an entry for that component will be added to the index using the org.springframework.stereotype.Component stereotype.
This annotation is also honored on meta-annotations. Consider this custom annotation:
@Indexed는 @Override처럼 명시를 한다. 인덱스라는 명시를 하고, 내부적으로 인덱싱을 한다.
스프링은 패키지들에 어노테이션이 붙은 컴포넌트를 스캔한다. 컴파일때 스프링은 인덱싱된 candidate components 즉, 컴포넌트 후보자들을 이용하여 빈들을 생성한다.
스프링은 @Indexed가 붙은 클래스들을 찾고 인덱스에 추가한다. 그리고 @Indexed가 붙은 어노테이션들에게 메타 어노테이션 권한을 부여한다.
메타 어노테이션이란 다른 어노테이션에 해당 어노테이션을 붙일 수 있게 해줘서 여러 어노테이션이 붙은 하나의 어노테이션을 사용자가 만들 수 있게 해준다.
예를 들어서 @Component어노테이션을 보겠다.
1
2
3
4
5
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Indexed
public @interface Component { }
@Component어노테이션이 붙은 그 어떤것도 컴포넌트 인덱스에 추가될 후보자가 된다. 비슷하게 @Repository, @Service도 결국 @Component가 명시되어있으므로 모두 컴포넌트 인덱스에 추가된다.
내가 만들고 있는 프로젝트의 경우 META-INF/spring.components 파일로 들어가면
1
2
3
com.javabyexamples.spring.core.beanindexing.indexedbased.UserController=org.springframework.stereotype.Component
com.javabyexamples.spring.core.beanindexing.indexedbased.UserServiceImpl=org.springframework.stereotype.Component
com.javabyexamples.spring.core.beanindexing.indexedbased.UserRepository=org.springframework.stereotype.Component
이런식으로 들어갈 것이다. 인터페이스랑 클래스에도 사용이 가능하며, 상속을 받을 수도 있다.
는 2편에서 계속 작성..
여담 및 결론
오래 안 걸릴줄 알고 회사 점심시간 1시간을 할애해서 작성하였는데, 생각보다 작성해야할 내용이 많았다. 그래서 집에서 추가로 2편을 작성해야할것 같다.
현재까지를 요약하자면 다음과 같다.
1
2
3
4
5
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@SpringBootApplication은
@Target을 통해 클래스위에 붙을 수 있음을 알려주고@Retention을 통해 런타임때까지 살아있음을 알려주고@Documented를 통해 Javadoc에 설명을 달아주고@Inherited를 통해 해당 어노테이션을 상속받아도 똑같이 적용되게 해주고@SpringBootConfiguration을 통해 설정값들을 스캔하고 이 어노테이션을 인덱스에 추가해 스프링이 뜰때 우선적으로 스캔할 수 있게한다.
Reference
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/java-target-annotations/ Target 어노테이션 타입표
- https://jeong-pro.tistory.com/234 Retention 설명 관련글.
- https://hongsii.github.io/2018/12/12/java-annotation/ Inherited어노테이션 예제
- https://livenow14.tistory.com/52 Spring 설정 계층
- https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/javadoc-api/org/springframework/stereotype/Indexed.html @Indexed javaDoc
- https://www.intertech.com/spring-4-meta-annotations/ what is meta Annotation