Programmers_hash04 - 베스트앨범
Programmers_hash04 - 베스트앨범
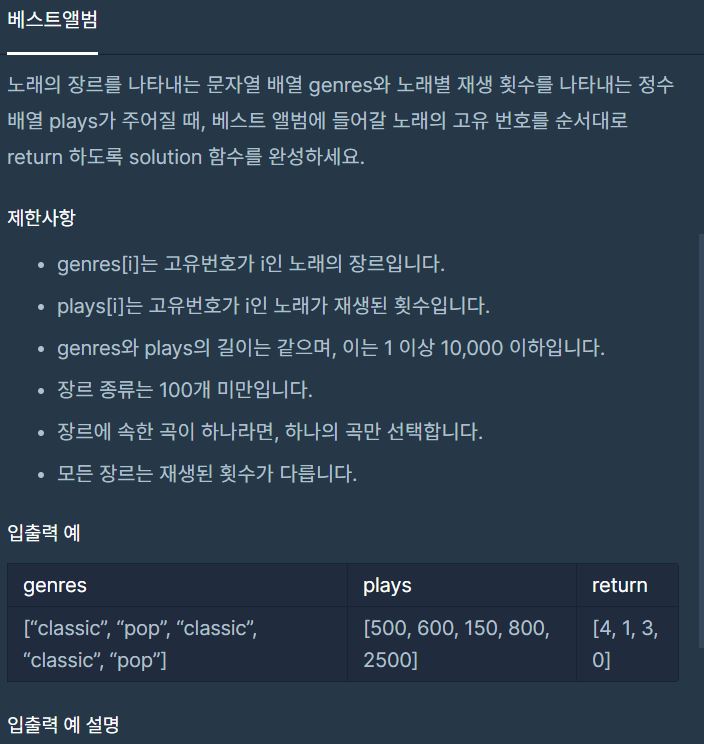
프로그래머스 -해시 - 베스트앨범 문제 입니다.
1. 문제
https://programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/parts/12077
2. 분류 및 난이도
Programmers 문제입니다. Level 3의 문제입니다.
3. 생각한 것들(문제 접근 방법)
- 생각해야할 게 너무 많습니다.
- 첫 번째로 장르에 대해 카운트 값을 관리해야하고(정렬 기준 1)
- 두 번째로 해당 장르에 대한 수록곡들의 재생횟수(정렬 기준 2)
- 세 번째로 장르들의 인덱스 값(값 도출에 인덱스를 넣어야하므로)
- 하지만 값들은 총 4가지로 (장르, 장르들의 합계, 수록곡의 재생목록, 인덱스) 이것을 다 관리할 수 있는 것이 c++에 있을까 생각했습니다.
- 없는 것 같습니다.
- 일단 map을 사용해서 장르들의 합계정보를 넣었습니다.
- map을 쓴 이유는 string에 대한 관리가 쉬워서 썼습니다.
- 또한 장르의 최대 갯수는 100개로 최악의 경우 1만개의 배열을 갖는 answer vector보다 작아 관리하기 쉽습니다.
- 문제는 map에 합계정보를 넣어도 합계정보인 value값으로 정렬이 되지 않아서 따로 vector에 넣어서 정렬해줘야합니다.
- 처음 벡터에는 장르,재생횟수,인덱스 정보를 넣어줬습니다.
- 벡터에 정보를 넣으면서 장르 map에도 합계 정보를 차곡히 쌓아줍니다.
- 장르를 기준으로 정렬을 하되(나중에 탐색 시 용이), 같은 장르인 경우 재생횟수, 재생횟수마저 같다면 작은 인덱스 기준으로 정렬을 해줬습니다.(밑의 pred함수)
- 장르 합계 map을 합계순을 정렬하기 위해 임시 벡터 (countvec)를 이용해서 합계순으로 정렬을 해줍니다.
- 정렬해준 벡터를 돌면서 이진 탐색을 통해 찾는 문자열에 대해 재생횟수가 많은 순으로 2번까지 해당 인덱스를 answer vector에 넣어줍니다. 만약 장르속에 수록곡이 1개인 경우도 예외처리 해줍니다.
4. 접근 방법을 적용한 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
bool pred(pair<pair<string, int>, int> pair1, pair<pair<string, int>, int> pair2)
{
if (pair1.first.first == pair2.first.first)
{
if (pair1.first.second == pair2.first.second)
return pair1.second < pair2.second;
else
return pair1.first.second > pair2.first.second;
}
else
return pair1.first.first < pair2.first.first;
}
bool countingvec(pair<string, int> a, pair<string, int> b)
{
return a.second > b.second;
}
int binarysearch(vector<pair<pair<string, int>, int>> vec, string str, int size)
{
int lower = 0;
int upper = size - 1;
int mid;
while (lower <= upper)
{
mid = (lower + upper) / 2;
if (str > vec[mid].first.first)
lower = mid + 1;
else
upper = mid - 1;
}
return lower;
}
vector<int> solution(vector<string> genres, vector<int> plays) {
vector<int> answer;
map<string, int> m;
vector<pair<pair<string, int>, int>> vec;
for (size_t i = 0; i < genres.size(); ++i)
{
//cout << vec[i].first.first << vec[i].first.second << vec[i].second << '\n';
vec.push_back(make_pair(make_pair(genres[i], plays[i]), i));
//map에 카운트 값을 넣는다. 맨처음꺼라면
if (m.find(vec[i].first.first) == m.end())
{
m.insert(make_pair(vec[i].first.first, vec[i].first.second));
}
else//찾았다면
{
m[vec[i].first.first] += vec[i].first.second;
}
}
sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), pred);
map<string, int>::iterator iter;
vector<pair<string, int>> countvec(m.begin(), m.end());
sort(countvec.begin(), countvec.end(), countingvec);
for (size_t i = 0; i < countvec.size(); ++i)
{
int range = 0;
string findstr = "";
findstr += countvec[i].first;
int index = binarysearch(vec, findstr, vec.size());
//cout << findstr << index << '\n';
for (; range < 2; ++range)
{
//1개인 경우
if (vec[index].first.first != findstr)
{
break;
}
else
{
answer.push_back(vec[index].second);
++index;
}
}
}
return answer;
}
5. 결과
어렵습니다.
시간도 1시간정도 걸렸습니다.
다른 사람들 어떻게 풀었나 대충 봤는데 비슷해서 다행이었습니다.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.